Scan
Introduction
In this example, we're going to set up the dongle using Python script to scan for nearby Bluetooth devices. For a quick setup, copy the following script and save it on your local directory. You can also get the source code from our GitHub page.
import serial
import time
connecting_to_dongle = 0
print("Connecting to dongle...")
# Trying to connect to dongle until connected. Make sure the port and baudrate is the same as your dongle.
# You can check in the device manager to see what port then right-click and choose properties then the Port Settings
# tab to see the other settings
while connecting_to_dongle == 0:
try:
console = serial.Serial(
port='COM14',
baudrate=57600,
parity="N",
stopbits=1,
bytesize=8,
timeout=0
)
if console.is_open.__bool__():
connecting_to_dongle = 1
except:
print("Dongle not connected. Please reconnect Dongle.")
time.sleep(5)
print("\n\nConnected to Dongle.\n")
print("\nWelcome to the Bluetooth device Scanning example!\n\n")
new_input = "NEW-INPUT"
while 1 and console.is_open.__bool__():
# get keyboard input once
if (new_input == "NEW-INPUT"):
# Python 2 users
# input = raw_input("Select:\n1) If you... ")
new_input = input("Select:\n1) If you'd like to scan for devices without a timer to stop.\n2)"
" If you'd like to scan for devices for a selected period of time.\n"
"3) If you'd like to scan a specific device.\n>>")
if new_input == "1":
time.sleep(0.1)
# sends the commands to the dongle. Important to send the \r as that is the return-key.
console.write(str.encode("AT+CENTRAL"))
console.write('\r'.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
console.write(str.encode("AT+GAPSCAN"))
console.write('\r'.encode())
elif new_input == "2":
time.sleep(0.1)
# sends the commands to the dongle. Important to send the \r as that is the return-key.
console.write(str.encode("AT+CENTRAL"))
console.write('\r'.encode())
input_time = input("Please select amount of time the scanning should continue: ")
while not input_time.isdigit():
input_time = input("Sorry, unacceptable time.\n"
"Please select amount of time the scanning should continue: ")
console.write(str.encode("AT+GAPSCAN="))
console.write(input_time.encode())
console.write('\r'.encode())
elif new_input == "3":
time.sleep(0.1)
# sends the commands to the dongle. Important to send the \r as that is the return-key.
console.write(str.encode("AT+CENTRAL"))
console.write('\r'.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
input_adress = input("Please enter type ([0] or [1]) and the address (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) of the device you "
"\nwish to scan (format:[x]xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx): ")
console.write(str.encode("AT+SCANTARGET="))
console.write(input_adress.encode())
console.write('\r'.encode())
else:
print("That was not a choice. Please choose one of the options.")
new_input="NEW-INPUT"
# let's wait one second before reading output (let's give device time to answer)
time.sleep(1)
out = ""
while console.inWaiting() > 0:
out += console.read(console.inWaiting()).decode()
else:
if not out.isspace():
# We make sure it doesn't print the same message over and over again by setting [out] to blankspace
# after printing once and check for blankspace before print again
print(out + " ")
out = " "
Open up the command prompt in the directory where the script is located. Start the script by typing
python scriptname.py
and press Enter.
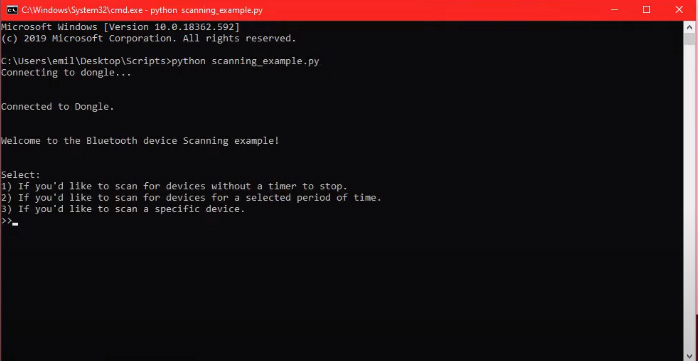
You should now be prompted to choose between three options.
- Scan without time limit. (requires no input)
- Scan with a time limit. ( requires an input a number representing the time in seconds.)
- Scan a specific devices advertising data. (requires an address to the desired Bluetooth device which we can get from the other two options)
Option 3 will show the full advertising and response data of 31 bytes from the selected device.
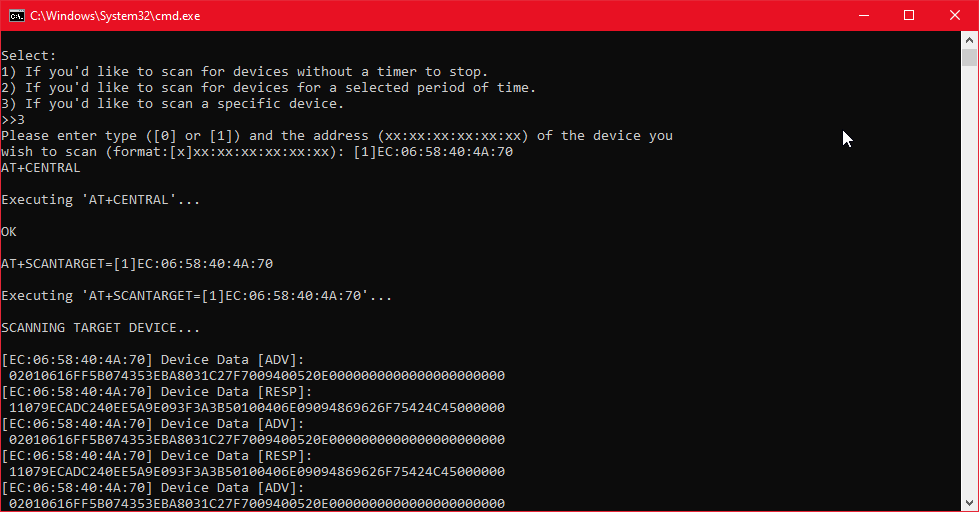
And that is how we scan for Bluetooth devices. If you want to stop the script, you can simply press control C.
Youtube Tutorial
Follow the Youtube tutorial.
